Scheduling audit engagements in GRCHub ensures proper planning, tracking, and execution of audits, whether they are internal or external. This guide will walk you through the process of scheduling an audit engagement step by step.
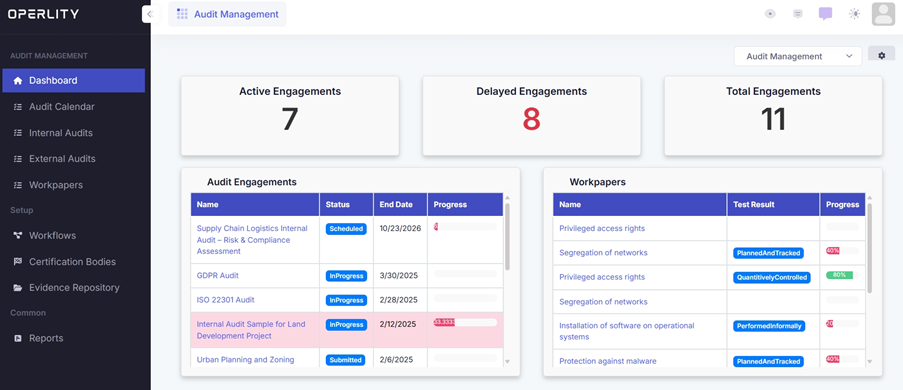
1. Navigating the Audit Management Module
To begin, navigate to the Audit Management Module from the left-hand menu. Here, you will find options for different types of audits:
- Internal Audits – Used to assess an organization's internal processes, compliance, and controls.
- External Audits – Used for audits conducted by third-party auditors or vendors.
Example:
If you need to conduct an internal audit to assess ISO 27001 compliance, select Internal Audits.
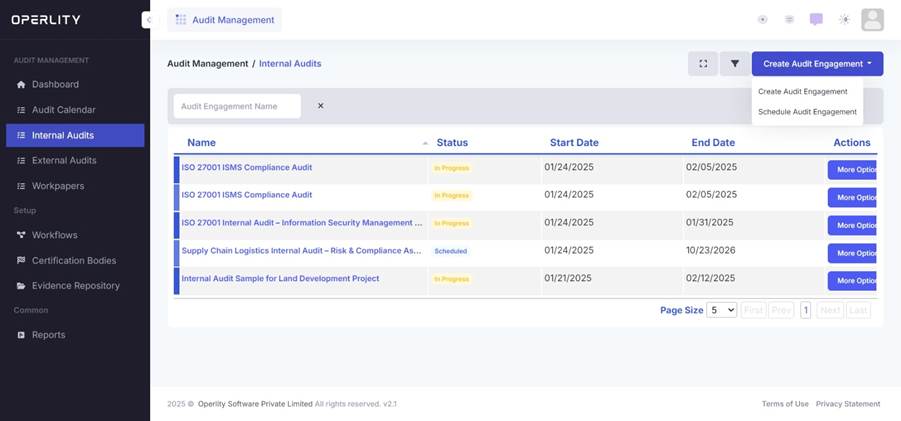
2. Scheduling an Audit Engagement
To schedule an audit, follow these steps:
- Click on "Create Audit Engagement" at the top-right corner of the screen.
- From the dropdown menu, select "Schedule Audit Engagement" (instead of creating an audit engagement).
- Fill in the following details:
- Audit Name – Provide a clear name for the audit.
- Description – Define the scope and purpose of the audit.
- Planned Start Date & End Date – Set the audit timeline.
- Audit Budget (if applicable) – Enter the estimated budget for the audit.
- Team Members – Add team members and assign roles (e.g., Audit Lead, Internal Auditors).
Example:
For an ISO 27001 ISMS Compliance Audit, you may assign an Audit Lead and Internal Auditors.
- Click "Continue" to proceed to the next step.
3. Defining the Audit Scope
The next step involves selecting the scope of the audit. GRCHub provides three scope options:
3.1 Control Implementation
- Select this option if the audit focuses on specific security controls.
- Choose the relevant control(s) to evaluate implementation effectiveness.
- Example: Auditing the implementation of Access Control Policies.
3.2 Standards
- Select this if you are auditing against a security framework (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR).
- Choose the relevant framework, and GRCHub will generate the necessary compliance control as workpapers.
- Example: Auditing against ISO 27001, which will populate all related controls as workpapers.
3.3 Risk Assessment
- Select this to audit a specific Risk Assessment and verify mitigation efforts.
- Example: Auditing a previous Third-Party Risk Assessment.
After selecting the scope, assign the Auditee and Sponsor (the individual responsible for the audit). Click "Submit" to finalize the scheduling.
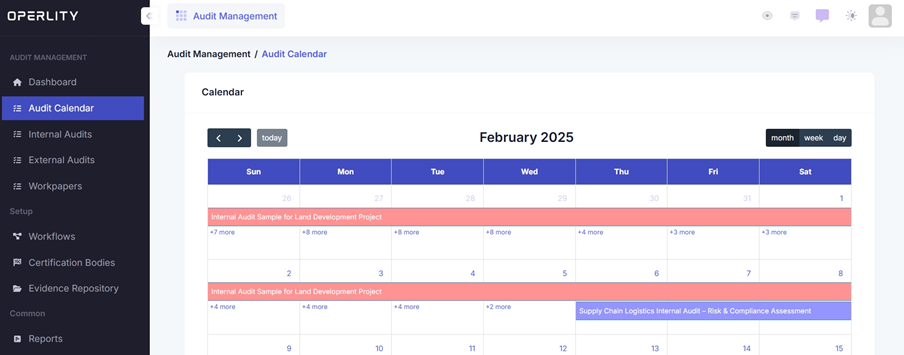
4. Tracking the Scheduled Audit
Once the audit has been scheduled, it will be visible in the Audit Calendar, where users can:
- View all upcoming audits.
- Track their status (e.g., Scheduled, In Progress, Completed).
- Manage audits efficiently by clicking on scheduled engagements.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article